What Is A Passive House?
A passive building is one that is built to rigorous standards for energy efficiency, health, comfort and durability. Utilizing passive building methodology is also one of the easiest ways of getting a home to net zero, in terms of annual energy needs. Passive building principles can be applied to all building types. The passive building standards and performance targets set for building certification are set and regulated by Phius.org — the leading North American organization conducting research, training and certification relating to passive buildings.
Radiation Control:
Achieved through climate specific window glazing based on glazing size and solar heat gain for not only windows but also doors. Shading strategies are also employed to prevent overheating in the cooling season and to help exploit the sun’s energy in the heating season.
Air Control:
Achieved by creating an airtight building envelope to prevent infiltration of outside air and to prevent loss of conditioned air. A balanced fresh air ventilation unit and filtration system, such as an ERV/HRV, is also employed. This unit exchanges stale indoor air for fresh outside air 24/7.

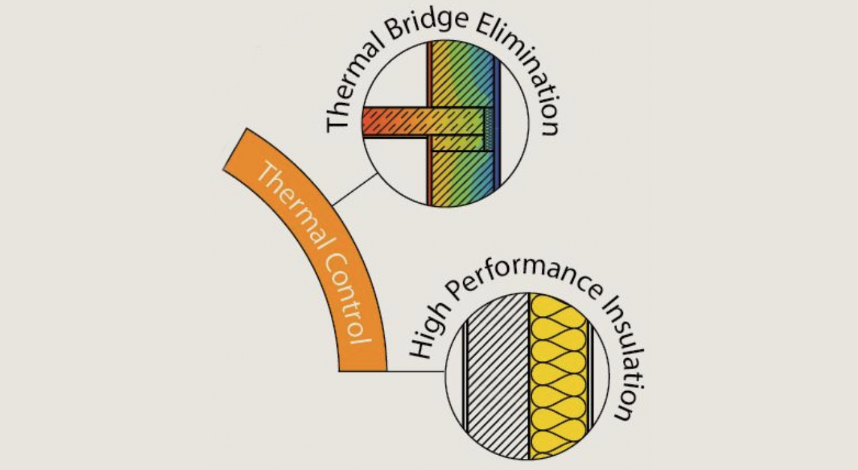
Thermal Control:
Achieved by continuous exterior insulation throughout the building envelope, typically above what is required by current building codes. Attention to detail is also given to areas with additional structure such as the sill plate, window headers, and top plates to avoid thermal bridging.
With these basic principles, passive buildings minimize energy demands and reduce the building operating costs permanently, while also dampening the impact of energy price increases over time. The low power requirements provide resilience during power outages and help avoid time of use surcharges. Adding a small renewable generation system such as solar PV to a passive building enables the owners to achieve a net zero/ positive home and a carbon-neutral lifestyle

